Veterinary orthopaedics
Angular deformity of both tibias. Pes Varus, bilaterally, open-wedge tibial osteotomy in two stages
Krzysztof Zdeb VS – LEGWET - Legionowo
Species: Dog
Sex: Male
Name: —
Breed: Dachshund
Age: 12 months, completed somatic growth
Health condition: —
Diagnosis
- angular deformity of both tibias. Pes Varus, bilaterally
- open-wedge tibial osteotomy in two stages
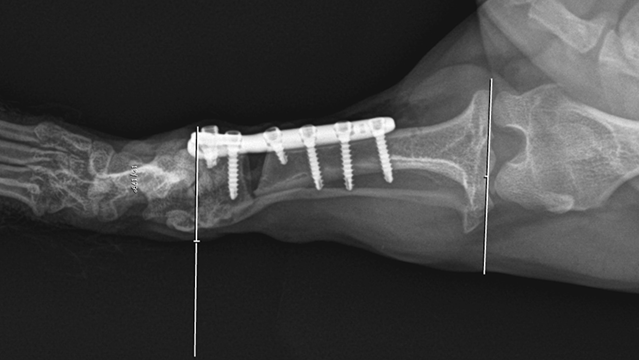
1. Radiological image of the right tibia after osteotomy.

2. Radiological image of the left limb after osteotomy with the defect filled using a FlexiOss®Vet preparation with PRP.
Treatment
Osteotomy of the right tibia by distraction according to the open-wedge technique. Stabilisation with a 2.4 mm titanium locking bridge plate.
After 4 weeks, left tibial osteotomy was carried out according to the procedure previously used on the right limb. A FlexiOss®Vet preparation soaked with PRP (platelet-rich plasma) from the patient’s own blood taken before the procedure was inserted into the osteotomy fissure.
Treatment results
A rapid recovery was observed after both osteotomies. The patient gradually started to put weight on the operated limb. They way patient moves has changed, with rabbit-like hopping becoming less frequent.
On the day of the osteotomy on the other side (left side), follow-up X-rays of the right side were performed (4 weeks after osteotomy). Progressive healing processes of the right tibia were noted, but the osteotomy fissure was still visible.
After a further 4 weeks, the patient was moving very well at the follow-up visit, putting weight on both pelvic limbs. There has been a complete change in how the patient moves – from rabbit-like hopping to alternate walking.
In the control X-ray of the left tibia, the osteotomy fissure was fully filled with a fresh bone scar. In the control X-ray of the right tibia, the osteotomy fissure was filled with a bone scar.
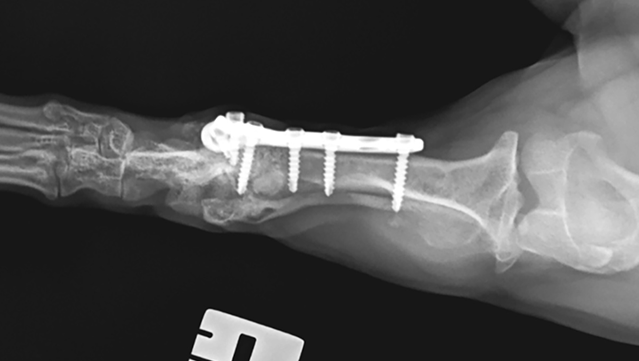
3. Radiological image of the left pelvic limb 4 weeks after osteotomy.
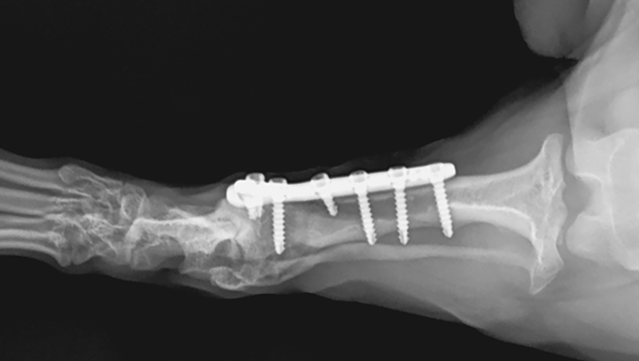
4. Radiological image of the right pelvic limb 8 weeks after osteotomy (4 weeks after osteotomy of the left limb).
Conclusions
Implantation of the FlexiOss®Vet preparation with PRP into the osteotomy fissure accelerated filling of the defect with bone scar, ensuring healing at 4 weeks after the procedure compared to the contralateral limb, where a similar radiological image was obtained at 8 weeks postoperatively.
Other cases
- All
- Veterinary orthopaedics
- Veterinary dentistry
- Horses
Veterinary orthopaedics
Angular deformity of both tibias. Pes Varus, bilaterally, open-wedge tibial osteotomy in two stages
Veterinary orthopaedics
Lameness of the right foreleg. Radioulnar mismatch at the elbow joint due to a short radius bone
Veterinary dentistry
Osteitis around canine 404, pulp necrosis of tooth 404, huge periapical lesion with partial lysis of the mandibular bone
Horses